As symbols of national pride, flags hold a special place in the hearts of people around the world. In Europe, a continent renowned for its rich history and diverse cultures, flags play a crucial role in representing the identity of each country. From the iconic tricolor of France to the regal Union Jack of the United Kingdom, European flags are a tapestry of colors and symbols that tell stories of heritage, unity, and aspirations.
In this comprehensive guide, we will dive into the fascinating world of European flags, exploring their design, symbolism, and historical significance. Whether you are a flag enthusiast, a student of European history, or simply curious about the banners that flutter across the continent, join us as we uncover the stories behind these emblematic flags.
Key Takeaways:
- European flags represent the unique identity and heritage of each country.
- Flags are symbols of unity, national pride, and aspirations for the future.
- Understanding the design and symbolism of European flags offers insights into the values and history of the countries they represent.
- The European Union flag symbolizes unity and cooperation among European nations.
- Exploring European flags provides a glimpse into the diverse cultures and histories of the continent.
The Design and Symbolism of the European Flag
The European flag is an emblem of great significance, crafted with a design that carries deep symbolic meaning. Its composition comprises a captivating circle of twelve golden stars against a serene blue backdrop. Delving into its symbolism reveals the essence of unity, identity, and aspirations embedded within this iconic banner.
Symbolic Representation
The twelve golden stars adorning the European flag hold immense symbolic weight. They represent the diverse peoples of Europe, symbolizing unity and solidarity. Each star stands for the indispensable notion of togetherness, reflecting the aspiration to foster a harmonious and cooperative European Union.
The Colors of the European Flag
The color blue forms the canvas upon which the golden stars shine brightly. Blue has long been associated with the Virgin Mary, signifying truth and intellect. In the context of the European flag, it represents the foundational values of the European Union: openness, enlightenment, and the pursuit of knowledge.
The golden hue of the twelve stars on the blue backdrop personifies glory and enlightenment. It radiates the collective achievements, potential, and aspirations of the European peoples. The golden stars gleam with the spirit of collaboration and progress, capturing the essence of a united Europe.
The Emblem’s Profound Significance
The European flag’s design and symbolism encapsulate the core values and principles of the European Union. It stands as a powerful representation of unity, peace, and the pursuit of shared goals. The golden stars evoke a sense of hope, while the blue background signifies the unwavering commitment to truth, intellect, and the common good.
As the European Union continues to shape the course of history, the flag serves as a reminder of the profound journey toward a more prosperous and harmonious Europe. It embodies the ideals and aspirations of a continent seeking a future founded on unity, cooperation, and shared destiny.
History of the European Flag
The history of the European flag dates back to 1955 when it was first adopted by the Council of Europe as a symbol for the entire continent. The flag, with its circle of twelve golden stars on a blue background, was intended to represent the unity and solidarity of the European peoples.
In 1985, the European flag gained further significance when it became the official emblem of the European Union. This adoption by the EU signaled the desire to see the flag used by other European organizations and highlighted its importance as a symbol of European identity and integration.
Although the European flag was planned to be included in the 2004 European Constitution, its adoption as an official symbol was not ratified. However, despite this setback, sixteen EU member countries and France have officially affirmed their attachment to the flag as a symbol of the European Union.
“The European flag represents the shared values, aspirations, and identity of the European peoples.”
The adoption of the European flag reflects the ongoing commitment to European unity and cooperation. It symbolizes the collective efforts of member countries to promote peace, stability, and prosperity on the continent.
The European flag serves as a powerful visual representation of the European Union, and it is proudly displayed at official buildings, international events, and in everyday life across Europe. Its presence reinforces the ideals of democracy, human rights, and shared prosperity that lie at the heart of the European Union.
“The European flag stands as a symbol of unity, peace, and collaboration in Europe.”
The Schengen Area and the European Flag
The Schengen Area, an area without borders where people can travel freely between member countries, has a close association with the European flag. Established in 1985, the Schengen Area currently includes 23 of the 27 European Union member states. The European flag holds a prominent position in Schengen Area countries, proudly displayed as a symbol of the region’s commitment to freedom of movement and unity.
The European flag’s presence in the Schengen Area reinforces the principles of collaboration, openness, and interconnectedness that underpin this unique and progressive zone. It serves as a visual representation of the values shared by member countries, promoting a sense of belonging and cooperation among nations. With its striking blue background and circle of golden stars, the flag captures the essence of European integration and the vision of a unified continent.
Freedom of Movement and Unity
One of the fundamental goals of the Schengen Area is the elimination of internal borders, allowing citizens to move freely without passport checks or other restrictions. By enabling seamless travel across its member countries, the Schengen Area promotes economic growth, cultural exchange, and closer ties among European nations.
The European flag in the Schengen Area serves as a powerful reminder of the region’s commitment to freedom of movement and unity. It symbolizes the collective endeavor to build a Europe without barriers and to foster a sense of shared identity and purpose.
The European flag’s presence throughout the Schengen Area reinforces the principle that Europeans are not bound by physical borders but are united by common values and aspirations, transcending national boundaries. It serves as an emblem of solidarity and cooperation, reflecting the inclusive and interconnected nature of the Schengen Area.
Symbolic Significance
Visually captivating and instantly recognizable, the European flag plays an essential role in creating a sense of belonging and shared purpose. Its symbolism extends beyond the Schengen Area, encompassing the entire European Union and its member countries. The flag represents the ideals of unity, peace, and cooperation that lie at the core of European integration.
“The European flag is a symbol of unity and cooperation, reflecting our shared belief in a continent united in diversity.” – Ursula von der Leyen
As Europeans travel freely across the Schengen Area, the sight of the European flag reminds them of the values that unite them and the vision of a Europe where diversity is celebrated and barriers are overcome. It stands as a powerful symbol of the ongoing journey towards a more integrated and prosperous European Union.
European Union Membership and the Flag
The European Union encompasses a collective of 27 member countries, each working collaboratively to promote peace, prosperity, and equality throughout the continent. While every member country proudly displays its own distinct flag, they also unite in their reverence for the European flag. Representing the shared identity and unity of the European Union, the European flag stands as a powerful symbol of collaboration and harmonious coexistence.
Flown alongside national flags, the European flag serves as a visual representation of the collective aspirations and values of the European Union. It is a testament to the strength found in diversity and the shared commitment to mutual respect and understanding. As member countries come together under the European flag, they reinforce their dedication to fostering a Europe that thrives on cooperation, solidarity, and the pursuit of a better tomorrow.
Whether it’s in official state ceremonies, international events, or everyday displays of national pride, the European flag stands as a prominent reminder of the shared journey that lies at the heart of the European Union. It exemplifies the spirit of unity and serves as a visual representation of the continent’s ongoing pursuit of a brighter and more inclusive future.
European Union Flags: A Comparative Overview
| Country | Flag |
|---|---|
| Austria | |
| Belgium | |
| Bulgaria | |
| Croatia | |
| Cyprus | |
| Czech Republic | https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SfoS1eXT36c |
| Denmark | |
| Estonia | |
| Finland | |
| France | |
| Germany | |
| Greece | |
| Hungary | |
| Ireland | |
| Italy |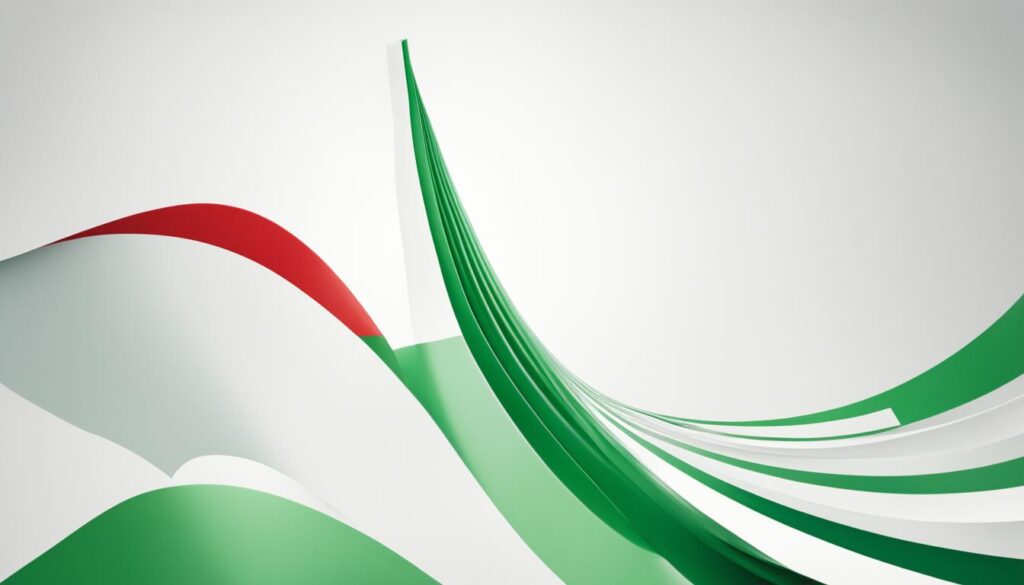  |
| Latvia | |
| Lithuania | |
| Luxembourg | |
| Malta | |
| Netherlands | |
| Poland | |
| Portugal | |
| Romania | |
| Slovakia |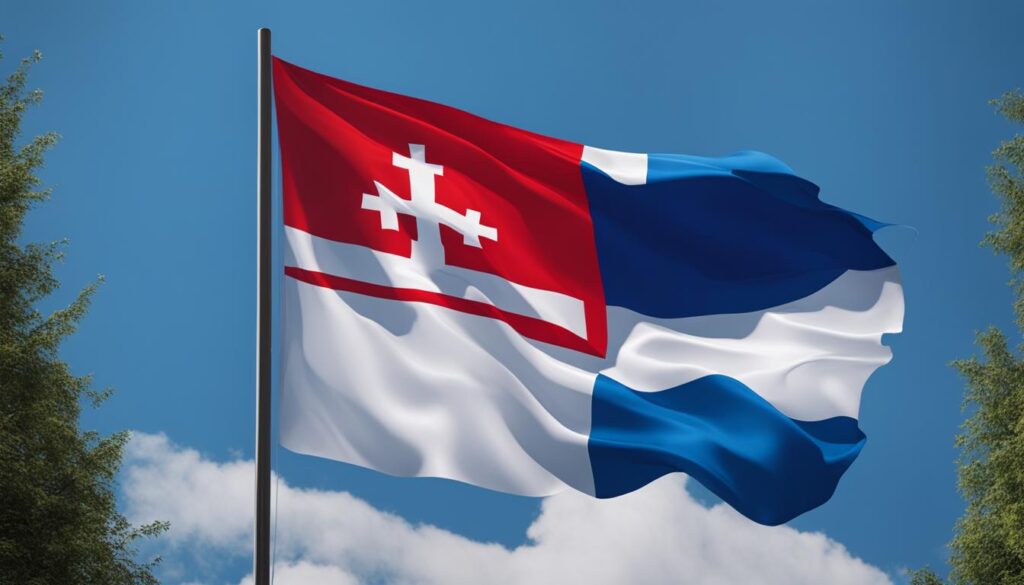  |
| Slovenia | |
| Spain | |
| Sweden |
The European Flag’s Importance to European Identity
The European flag plays a significant role in shaping European identity. It is a powerful symbol that represents the shared values, heritage, and aspirations of the European people. The flag can be seen on official buildings, at international events, and in everyday life across the continent.
The European flag serves as a visual reminder of the unity and cooperation among European nations. It symbolizes the collective identity of the European Union and inspires a sense of belonging and pride in being European. The flag’s design, with its circle of twelve golden stars on a blue background, embodies the ideals of unity and harmony that Europe strives to achieve.
European flag images and vectors are widely available, allowing individuals and organizations to incorporate the flag into various projects and initiatives. From website banners to promotional materials, the use of European flag images helps to reinforce the message of unity and solidarity.
The Role of European Flag Images
The availability of European flag images in various formats, including vector files, allows for easy customization and integration into different designs. These images can be used in graphic design, advertisements, social media campaigns, and educational materials to visually communicate the European identity and promote the values of the European Union.
By using European flag images, individuals and organizations can visually represent their support for European unity and cooperation. Whether it’s displaying the flag on a website or incorporating it into a logo, these images reinforce the message of inclusivity and working together for a better Europe.
“The European flag represents the unity and cooperation among European nations, showcasing the shared values and aspirations of the European people.”
Symbolizing Unity and Cooperation
The European flag serves as a unifying symbol, reminding Europeans of their common interests and the importance of collaboration. It promotes a sense of belonging to a larger European community, transcending national boundaries and fostering cultural exchange.
Moreover, the presence of the European flag at significant international events further highlights the unity and influence of the European Union on the global stage. It symbolizes Europe’s commitment to working together to address common challenges and pursue shared goals, such as peace, prosperity, and sustainable development.
Ultimately, the European flag’s prominence in public spaces and its widespread use in various contexts contribute to the cultivation of a strong European identity. It reinforces the idea that Europe is more than a collection of individual countries but a unified entity striving for a brighter future together.
The European Union’s Efforts for Peace
The European Union (EU) has been actively committed to maintaining peace in Europe since its establishment. Through its efforts, the EU has played a vital role in preventing conflicts between member countries and fostering mutual understanding and cooperation.
Recognizing the EU’s contribution to peace, it was awarded the Nobel Peace Prize in 2012, further highlighting its significant impact. This prestigious recognition reflects the EU’s dedication to promoting harmony and unity within the European region.
“The European Union’s tireless efforts in building and preserving peace among its member states have been crucial in maintaining stability and ensuring a prosperous future for Europe.”
The European Union’s commitment to peace is symbolized by the European flag. The flag serves as a reminder of the importance of unity and collaboration in fostering a peaceful future for Europe.
| Key Achievements | Impact on Peace |
|---|---|
| Establishment of the European Coal and Steel Community (ECSC) | Promoted economic cooperation, reducing the likelihood of conflicts over key resources. |
| Creaton of the European Economic Community (EEC) | Developed a single market, facilitating trade and fostering economic stability among member countries. |
| Expansion of the EU | Provided opportunities for reconciliation and cooperation among previously divided nations. |
| Peacekeeping Efforts | Supported peacekeeping missions in conflict-affected regions, contributing to stability and peace restoration. |
The European Union’s commitment to peace extends beyond its borders. The EU actively engages in diplomatic efforts and collaborates with international organizations to promote peaceful resolutions to global conflicts.
The European Union as a Role Model for Peace
By successfully fostering peace and stability among member countries, the European Union has become a role model for other regions facing similar challenges.
- Its framework and institutions offer a blueprint for cooperation and peaceful coexistence.
- The EU’s commitment to diplomacy and dialogue serves as an example for resolving conflicts peacefully.
- The European Union’s continuous efforts to bridge divides and promote understanding contribute to a more peaceful and interconnected world.
Through its unwavering dedication to peace, the European Union continues to shape Europe’s future, ensuring a continent firmly rooted in unity, cooperation, and tranquility.
European Union Values and the Flag
The European Union is founded on a set of core values that form the basis of its identity and purpose. These values are enshrined in the EU’s treaties and shape its policies and actions. The European flag serves as a powerful symbol of these ideals, representing the commitment to a Europe where democracy, human rights, equality, and the rule of law are fundamental.
Democracy lies at the heart of the European Union, with the belief that decisions should be made through open and fair processes, ensuring the participation and representation of all citizens. The European flag stands as a reminder of the EU’s dedication to upholding democratic principles and fostering active citizenship.
Respect for human rights is a cornerstone of the European Union’s values. The EU is committed to protecting the rights and dignity of every individual, promoting equality and non-discrimination. The European flag embodies this commitment, representing a Europe that values the inherent worth and rights of all its people.
Equality is a fundamental principle of the European Union, aiming to ensure that all individuals have equal opportunities and treatment. The European flag is a symbol of the EU’s pursuit of a just and inclusive society, where everyone is respected and valued regardless of their background, gender, religion, or any other characteristic.
The rule of law is essential for the functioning of a democratic society and the protection of rights and freedoms. The European Union upholds the principle of the rule of law, promoting legal certainty, accountability, and the fair application of laws. The European flag represents the EU’s commitment to a Europe governed by just and transparent legal systems.
“The European flag is a powerful symbol of the values that bind the European Union together. It represents our shared commitment to democracy, human rights, equality, and the rule of law. It serves as a constant reminder of the importance of upholding these ideals and working together for a better future.” – President of the European Commission
The European flag is more than just a piece of cloth. It carries a profound message of unity, progress, and the pursuit of a Europe that values the dignity and rights of all its citizens. As the flag waves proudly across the European Union, it serves as a visual representation of the shared values and aspirations that unite the diverse nations of Europe.
The Anthem and Motto of the European Union
The European Union has an official anthem known as the “European Anthem” or “Ode to Joy,” which is based on the final movement of Ludwig van Beethoven’s Ninth Symphony. It was adopted in 1985 as the official anthem of the European Union and represents the values of freedom, peace, and solidarity.
The European Union’s motto, “United in Diversity,” emphasizes the importance of different cultures and languages coming together in harmony.
The European Anthem or “Ode to Joy,” composed by Beethoven, is a powerful musical composition that has become synonymous with the European Union. It serves as a unifying force, evoking emotions of joy, hope, and togetherness. The anthem represents the shared aspirations and values that are pivotal to the European Union’s vision of a united and peaceful Europe.
The European Union’s motto, “United in Diversity,” captures the essence of the Union’s core principle. It highlights the recognition and celebration of the different cultures, traditions, and languages found within the European Union. The motto exemplifies the Union’s commitment to fostering unity while embracing and respecting the rich diversity that exists among its member countries.
| Anthem | Motto |
|---|---|
| Ode to Joy | United in Diversity |
The European Union’s Institutions
The European Union (EU) is governed by several key institutions that collectively shape its policies and decision-making processes. These institutions play a vital role in promoting collaboration, unity, and effective governance within the EU. The three main institutions are the European Commission, the European Parliament, and the Council of the European Union.
The European Commission
The European Commission is the executive branch of the European Union. It is responsible for proposing and implementing laws and policies that promote the interests of the EU and its member countries. The Commission consists of a group of appointed commissioners, each assigned a specific portfolio, such as trade, environment, or economy. As the driving force behind EU legislation, the European Commission ensures that the Union functions efficiently and effectively.
The European Parliament
The European Parliament represents the interests of the citizens of the European Union. It is composed of directly elected members from each member state. The Parliament debates and votes on proposed legislation, ensuring that the voices and concerns of European citizens are heard and taken into account. As an important democratic institution, the European Parliament plays a crucial role in shaping EU policies and legislation.
The Council of the European Union
The Council of the European Union, also known as the Council of Ministers, is composed of representatives from each member country’s national government. It is responsible for making decisions on EU legislation, adopting budgets, and coordinating policies among member states. The Council plays a key role in the EU’s decision-making process, representing the diverse interests and perspectives of individual countries.
The European flag, with its circle of twelve golden stars on a blue field, is prominently displayed in these institutions, symbolizing their commitment to European unity, collaboration, and the shared values of the European Union.
| Institution | Role |
|---|---|
| European Commission | Proposing and implementing laws and policies |
| European Parliament | Representing the interests of European citizens |
| Council of the European Union | Making decisions on EU legislation and coordinating policies |
The European Union and the Euro
The European Union (EU) has established its own currency, the euro, which is widely used across member countries. Currently, 19 out of the 27 EU member countries have adopted the euro as their official currency. The introduction of the euro has played a significant role in promoting easier trade and fostering economic integration within the European Union.
The euro enables seamless transactions between member countries, eliminates currency exchange costs, and reduces fluctuations in exchange rates. This has facilitated business activities, enhanced cross-border investments, and contributed to the overall growth of the European economy. The euro’s stability and acceptance have made it a reliable currency for international trade and investments.
The European flag is often associated with the euro, representing the economic unity and cooperation among member countries. The flag, with its circle of twelve golden stars on a blue background, symbolizes the shared values and aspirations of the European Union, including its economic endeavors. It serves as a visual reminder of the EU’s commitment to collaboration, growth, and prosperity.
Having a single currency has not only strengthened economic ties within the EU but also promoted a sense of belonging and unity among member countries. Through the euro, individuals, businesses, and governments are connected in a common monetary system, fostering a deeper integration and interdependence. This has resulted in increased opportunities for trade, investment, and economic development.
The euro has become an internationally recognized currency, and its influence extends beyond the European Union. It is often used as a reserve currency by central banks and is traded on global foreign exchange markets. The euro’s stability and strength reflect the economic power and potential of the European Union.
The adoption of the euro has not been without challenges, such as the need for coordinated monetary policies and effective governance. However, the benefits of a common currency and the economic unity it fosters outweigh the challenges. The euro continues to play a crucial role in promoting economic stability, growth, and cooperation within the European Union.
| Benefits of the Euro | Challenges of the Euro |
|---|---|
| Enhanced trade opportunities within the EU | The need for coordinated monetary policies |
| Elimination of currency exchange costs | Effective governance of the eurozone |
| Reduced fluctuations in exchange rates | Harmonization of economic policies |
| Increased investment and economic integration | Ensuring financial stability |
The euro and the European flag are intertwined symbols of the economic unity and cooperation within the European Union. They represent the commitment to shared prosperity, growth, and stability among member countries. Through the adoption of the euro and the promotion of economic integration, the European Union continues to strive towards a stronger and more prosperous Europe.
European Union Expansion and Future Membership
The European Union (EU) has experienced significant expansion since its inception, with several countries joining in recent years. Notable additions to the EU include Croatia, Bulgaria, and Romania, all of which have become members in recent times. However, the expansion of the European Union is an ongoing process, and there are numerous countries, particularly in the Western Balkans and Eastern Europe, that aspire to join the EU in the future.
The prospect of future membership in the European Union holds significant importance for these countries. It represents an opportunity to benefit from the economic stability, prosperity, and democratic values that the EU strives to foster across the continent.
| Country | European Union Aspiration |
|---|---|
| Albania | Aspires to join the EU; has applied for membership. |
| North Macedonia | Has obtained candidate status and is engaged in accession negotiations. |
| Serbia | Has obtained candidate status and is engaged in accession negotiations. |
| Montenegro | Has obtained candidate status and is engaged in accession negotiations. |
| Bosnia and Herzegovina | Aspires to join the EU; has submitted its application. |
These aspiring EU members recognize that joining the European Union would not only bring economic advantages but also promote stability and enhance democratic governance within their countries. The EU’s comprehensive assistance packages and cooperative frameworks support these countries in meeting the necessary criteria for membership.
The European flag, with its circle of twelve golden stars on a blue field, symbolizes the European Union’s commitment to unity, stability, and prosperity. It serves as a symbol of hope for countries seeking membership and represents the EU’s dedication to fostering collaboration and democratic values across Europe.
Conclusion
The European flag is a powerful symbol that represents european unity and european identity. It stands as a testament to the shared values, aspirations, and identity of the European peoples. The flag’s design, featuring a circle of twelve golden stars on a blue field, signifies unity, solidarity, and harmony among the diverse nations of Europe.
The European flag serves as a constant reminder of the importance of collaboration, respect, and understanding among nations in shaping a harmonious and prosperous continent. It encapsulates the spirit of European integration and the commitment to building a better future together. By flying the flag, European countries reaffirm their dedication to fostering peace and cooperation, both within the European Union and among European nations at large.
As a symbol of unity and cooperation, the European flag plays a crucial role in shaping European identity. It is proudly displayed on official buildings, at international events, and in everyday life across the continent. The flag serves as a unifying force, reminding European citizens of their shared heritage and the values that bind them together. It stands as a symbol of hope, inspiring the pursuit of a Europe where diversity is celebrated and unity prevails.