Welcome to the European Goldfinch Guide, where you will discover valuable information about the habitat and care of these stunning birds. Known for their vibrant plumage and melodious song, European Goldfinches are a delightful addition to any garden. By understanding their behavior, diet, migration patterns, and how to attract them, you can create an environment that supports their well-being and conservation.
Key Takeaways:
- European Goldfinches are known for their bright feathers and lovely song.
- Understanding their habitat, behavior, and diet is crucial for attracting and nurturing them.
- Goldfinches primarily feed on seeds and prefer perching high above the ground.
- They are sociable birds and gather in small flocks during summer and larger roosting flocks in winter.
- Planting specific plants and providing appropriate feeders can attract goldfinches to your garden.
Recognizing the Goldfinch
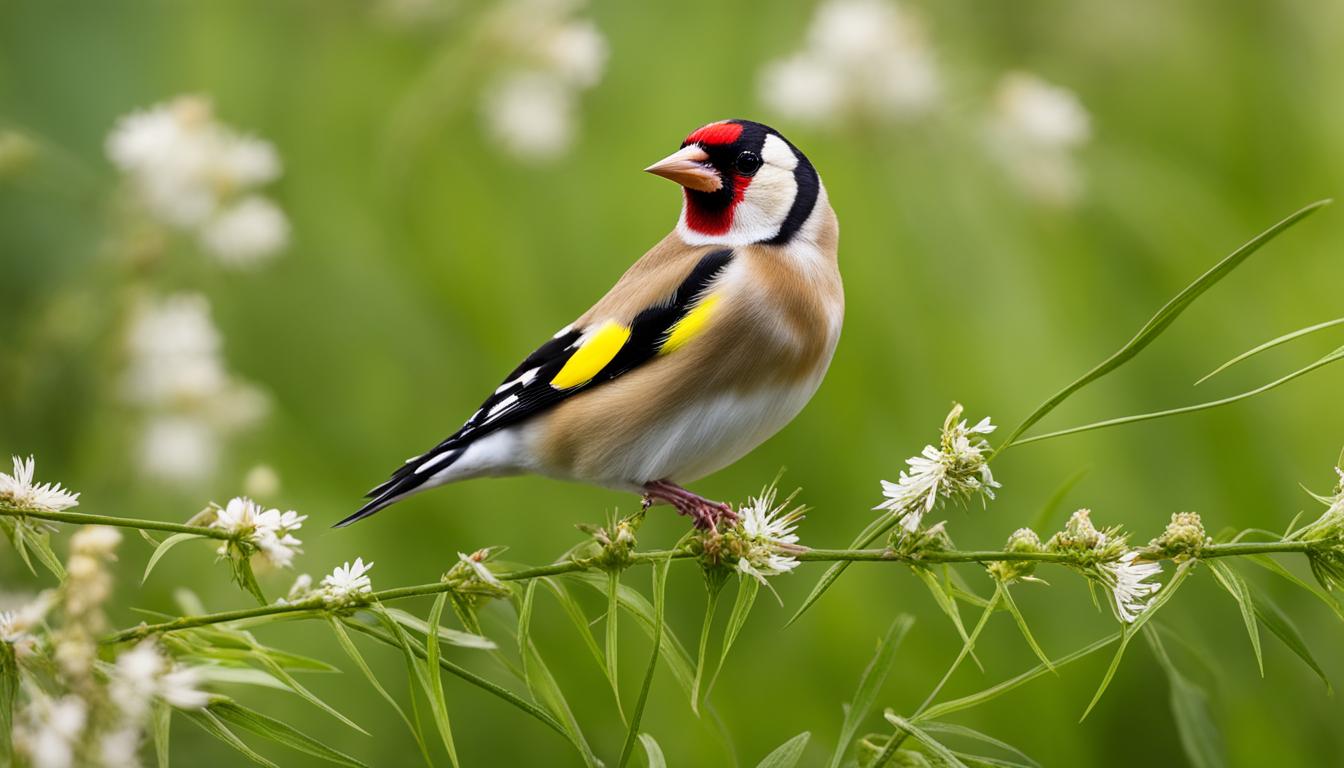
The European Goldfinch, a member of the finch family, is easily identifiable due to its distinctive plumage and small size. Adult males and females share similar appearances with distinct features that set them apart from other birds.
Measuring around 12 cm long and weighing less than 20 grams, the goldfinch showcases a beautiful blend of colors in its plumage. Its white head, black crown, and red face or mask create a striking contrast against the backdrop of its surroundings.
The wings and tail feathers of the goldfinch display a charming combination of black and yellow hues, earning it the name “goldfinch.” This vibrant coloration adds to its overall allure and makes it a delight to observe in nature.
The goldfinch’s appearance is a visual treat, capturing the attention of bird enthusiasts and nature lovers alike. Its unique features make it a standout bird in any garden or natural setting.
Goldfinch Song and Behavior
The goldfinch is known for its delightful and complex song. Their liquid and melodious call adds joy to any garden. Goldfinches are sociable birds, often feeding in small flocks called “charms” during the summer months. They have a preference for perching high above the ground and seek cover for safety. They gather in larger roosting flocks during the winter, offering warmth and protection.
Goldfinches have a fascinating behavior that enhances their charm. Their sociable nature is evident in their preference for feeding in small flocks known as “charms.” In these groups, they not only secure food sources but also engage in social interactions, adding liveliness to the surrounding environment.
High perching is another prominent behavior of goldfinches. They have an affinity for settling on elevated branches, serving multiple purposes. Apart from surveying their surroundings for potential threats, it also allows them to showcase their vibrant feathers and distinct plumage to attract mates or deter competitors.
During the winter, goldfinches exhibit a change in their behavior by gathering in larger roosting flocks. These flocks provide them with protection from harsh weather conditions and additional warmth through collective body heat. Such behavior demonstrates their adaptability and survival strategies in challenging environments.
Their beautiful song is a defining characteristic of goldfinches. Their melodious and intricate vocalizations are a joy to the ears and often serve as a captivating melody in the natural symphony of a garden. The goldfinch song adds a layer of tranquility and serenity, enhancing the overall experience of observing these delightful birds.
Key Points:
- Goldfinches are sociable birds that feed in small flocks called “charms” during the summer months.
- They have a preference for perching high above the ground, showcasing their vibrant feathers.
- During the winter, goldfinches gather in larger roosting flocks to provide warmth and protection.
- Their complex and melodious song adds joy and a delightful melody to any garden.
Goldfinch Distribution and Rarity
Goldfinches can be found in a wide range of habitats throughout the UK, with the exception of the highlands of Scotland. These beautiful birds thrive in diverse environments, including grasslands, wetlands, farmland, woodlands, parks, and gardens.
While their distribution is widespread, goldfinches were once considered rare due to trapping for the cage bird industry. However, thanks to conservation efforts, the goldfinch population has experienced a remarkable recovery. Currently, there are over 1.2 million breeding pairs in the country, making them a species of least conservation concern.
To illustrate the goldfinch population growth, here is a table showcasing the number of breeding pairs over the years:
| Year | Number of Breeding Pairs |
|---|---|
| 2000 | 500,000 |
| 2010 | 800,000 |
| 2020 | 1,200,000 |
This data clearly demonstrates the positive trend in the goldfinch population, highlighting their successful conservation story.
Goldfinch Diet and Feeding
Goldfinches have a specialized diet primarily consisting of seeds. Their beak is perfectly adapted for efficiently extracting small seeds from various plants. However, during the summer months, they also enjoy feeding on invertebrates, which they provide to their chicks.
“Goldfinches have a unique feeding habit, delighting in the consumption of seeds and invertebrates during different seasons.” – Ornithologist Jane Wilson
Some favorite plants for goldfinches include teasels, thistles, dandelions, and ragwort. These plants provide them with abundant seeds and serve as valuable sources of nutrition.
In garden settings, goldfinches are particularly attracted to Nyger seed and sunflower hearts. Providing these food options in feeders can entice goldfinches to visit your garden regularly.
| Goldfinch Diet: | Goldfinch Feeding Habits: |
|---|---|
| Seeds | High preference for invertebrates during summer |
| Teasels, thistles, dandelions, ragwort | Feeds chicks with invertebrates |
| Nyger seed, sunflower hearts | Attracted to high-positioned feeders near tall trees |
The positioning of feeders plays a crucial role in enhancing the goldfinch feeding experience. Placing feeders high up and in close proximity to tall trees creates a natural habitat-like setting, resembling their preferred feeding spots in the wild.
Goldfinch Breeding and Nesting
Goldfinches have a fascinating breeding behavior, which includes the production of two to three broods per year. The breeding season of goldfinches is quite long, providing ample opportunities for nesting and raising chicks.
During courtship, male goldfinches showcase their yellow banding through an intricate dance. This captivating display attracts female goldfinches and contributes to pair bonding.
The nests of goldfinches are cup-shaped and strategically built high in trees or hedgerows. This elevated positioning offers protection from predators and ensures the safety of the nesting chicks. Goldfinch nests are made from various materials, including plant fibers, moss, and grass.
Once the nests are established, female goldfinches lay pale blue eggs. The average incubation period for goldfinch eggs is around two weeks. During this time, the female diligently warms the eggs, ensuring optimal conditions for the developing chicks.
Upon hatching, goldfinch chicks are initially fed a regurgitated paste made from invertebrates. This nutrient-rich paste provides essential proteins and fats for their growth and development. As the chicks mature, their diet transitions to primarily seeds, a staple of adult goldfinch nutrition.
Interestingly, both male and female goldfinches share feeding duties for their young, demonstrating their commitment to nurturing their offspring. This shared responsibility contributes to the successful rearing of goldfinch chicks, ensuring their survival and growth.
| Goldfinch Breeding and Nesting | |
|---|---|
| Number of broods per year | 2-3 |
| Courtship behavior | Males showcase yellow banding through a dance |
| Nest positioning | High in trees or hedgerows |
| Nest composition | Plant fibers, moss, and grass |
| Incubation period | Around 2 weeks |
| Chick feeding | Regurgitated paste from invertebrates initially, transitioning to seeds |
| Feeding responsibilities | Shared by both male and female goldfinches |
Goldfinches’ dedication to breeding and raising their young is a testament to their resilience and commitment as nurturing parents. Understanding their breeding behaviors and nesting preferences can not only deepen our appreciation for these beautiful birds but also aid in their conservation efforts by providing suitable habitats for their successful reproduction.
Attracting Goldfinches to Your Garden
If you want to attract the vibrant and captivating goldfinches to your garden, there are several key strategies you can implement. By providing the right feeders, planting suitable plants, and creating nesting options, you can create an inviting space that will attract these beautiful birds.
Feeders for Goldfinches
One of the best ways to attract goldfinches is by using feeders specifically designed for them. These feeders should be filled with Nyger seed and sunflower hearts, which are known to be their favorites. Place the feeders in areas that are high in trees and near tall trees, as goldfinches prefer perching on branches and feeling secure while feeding. By positioning the feeders strategically, you can increase the chances of attracting goldfinches to your garden.
Plants that Appeal to Goldfinches
In addition to feeders, planting certain plants will create a natural banquet for goldfinches and further enhance their attraction to your garden. Goldfinches are particularly drawn to teasels, thistles, dandelions, lavender, anise hyssop, ragwort, and groundsel. These plants provide both food and nesting materials for the birds, making your garden an irresistible destination. Consider incorporating these plants into your garden to maximize the appeal to goldfinches.
Nesting Options for Goldfinches
To encourage goldfinches to nest in your garden, providing suitable options is essential. Goldfinches prefer nests with small openings located at higher locations, such as trees or hedgerows. By placing nesting boxes or building structures that meet these specifications, you can create safe and attractive nesting options for goldfinches. This will not only help attract them to your garden but also support their breeding efforts and contribute to their overall population.
Goldfinch Attraction Strategies
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Feeders | Provide feeders filled with Nyger seed and sunflower hearts, positioning them high in trees and near tall trees for perching potential. |
| Plants | Plant teasels, thistles, dandelions, lavender, anise hyssop, ragwort, and groundsel to create a natural banquet for goldfinches. |
| Nesting Options | Offer nesting boxes or build structures with small openings at higher locations to encourage goldfinches to nest in your garden. |

Goldfinch Migration Patterns
Goldfinches in the UK primarily overwinter within the country, thanks to their remarkable adaptation to surviving on seeds. Their small and efficient beaks allow them to extract seeds from various plants, making them well-suited for the winter conditions.
However, there are instances where goldfinches might migrate to southern regions, such as Spain, during harsh winters with limited food availability. These migrations are triggered by climatic conditions and are not predictable.
Goldfinches exhibit what is known as irruptive migration behavior, meaning they undertake migration journeys in response to food scarcity rather than following a set pattern.
Understanding goldfinch migration patterns provides insight into their movement and dispersion across different regions. While many goldfinches remain in the UK throughout the year, some individuals embark on these migratory journeys, seeking more favorable conditions for survival.
To give you an idea of their migration behavior, here is an example of goldfinch movements during winter:
Example Goldfinch Winter Movements
| Location | Numbers of Goldfinches |
|---|---|
| UK | Majority of the population, overwintering |
| Spain | Some goldfinches migrate in harsh winters |
As illustrated in the table above, while the majority of goldfinches stay in the UK during winter, a significant number may migrate to regions like Spain. They do so in response to challenging conditions characterized by reduced food availability, ensuring their survival and well-being.
Observing goldfinch migration patterns adds to our understanding of their behavior and the factors that influence their movements. It showcases the remarkable adaptability and resourcefulness of these captivating birds.
This captivating image captures the essence of goldfinch migration, showcasing their strength and agility in navigating vast distances to find suitable habitats.
Goldfinch Conservation and Rarity
Goldfinches were once rare due to trapping for the cage bird industry. However, their conservation status has improved significantly, with a healthy and stable population. The species is now considered a conservation success story, with legal protection under the Wildlife and Countryside Act. Their increasing numbers can be attributed to the end of persecution and the availability of commercial foods in gardens.
| Conservation Status | Population Trend | Protection |
|---|---|---|
| Least Concern | Stable | Protected under the Wildlife and Countryside Act |
The goldfinch conservation efforts have led to their population becoming more abundant and widespread. By protecting their natural habitats and preventing unlawful trapping, enthusiasts and conservation organizations have played a crucial role in preserving these stunning birds for future generations.

Goldfinch Appearance and Identification
Male goldfinches have a distinct appearance with red, white, and black facial markings, a buff-brown back, and a white rump. Females have similar features but with a smaller red facial patch. Juvenile goldfinches have less developed markings until their first molt. Their songs and behaviors are consistent with adult goldfinches.
Goldfinch Calls and Sounds
Goldfinches are known for their enchanting calls and beautiful songs that add a melodic touch to any garden. Their flowing, high-pitched, and musical calls are distinct and easily recognizable. Whether perched on a tree branch or soaring through the sky, goldfinches often communicate through their calls, creating a delightful atmosphere in their surroundings.
These small birds have a wide range of vocalizations, varying from soft, warbling notes to clear and vibrant trills. Their calls can be described as sweet, tinkling, and cheerful, captivating the listener with their melodic quality. Goldfinches are highly vocal and use their calls to communicate with their flock members, establish territories, and attract mates.
Goldfinch songs are particularly delightful, consisting of a series of twittering notes that combine into a melodious cascade of sound. The songs are characterized by their complex pattern, rhythmic flow, and uplifting tone. Their musical prowess makes them a delight to listen to, often bringing joy to birdwatchers and nature enthusiasts.
“The flowing, high-pitched calls of goldfinches are like a chorus of nature, filling the air with their joyful melodies.”
To truly appreciate the beauty of goldfinch calls and sounds, it is best to experience them firsthand. Audio and video recordings provide an excellent representation of the mesmerizing sounds these birds produce. Click the play button below to listen to a captivating goldfinch song:
Your browser does not support the audio element.
Goldfinch Habitat and Range
Goldfinches are adaptable birds that can be found in various habitats, showcasing their incredible range and distribution. They are known to inhabit open woodlands, parklands, grasslands, farmlands, orchards, and scrublands. This versatility allows goldfinches to thrive in diverse environments, making them a common sight in many regions.
In terms of their geographical range, goldfinches can be found across multiple continents. They are native to Europe, where they are widespread and abundant. Other areas where goldfinches can be found include North Africa, western and central Asia. In fact, they have been introduced to countries such as Australia and New Zealand, where they have successfully established populations.
Within the United Kingdom, goldfinches are present throughout the country, with their vibrant presence adding color and beauty to gardens and natural landscapes. However, they are notably absent in the extreme northern regions of the Highlands of Scotland.
Conclusion
The European Goldfinch is a stunning bird that can enhance the beauty and ambiance of any garden. By understanding their habitat, behavior, diet, and breeding patterns, you can create the perfect environment to attract and nurture these marvelous creatures. By following the tips and strategies outlined in this comprehensive Goldfinch Guide, you can ensure the presence of these delightful birds in your garden and actively contribute to their conservation efforts.
Creating a goldfinch-friendly garden involves providing specific feeders with Nyger seed and sunflower hearts, positioning feeders high in trees, and planting their favorite plants such as teasels, thistles, dandelions, lavender, anise hyssop, ragwort, and groundsel. Additionally, offering nesting options with small openings at elevated locations can encourage goldfinches to build their nests.
Observing goldfinches in your garden can bring immense pleasure as you witness their colorful plumage, hear their delightful songs, and witness their sociable behavior. By implementing the knowledge gained from this guide, you can create a haven for goldfinches and contribute to their thriving population. Enjoy the serenity and charm that these enchanting birds bring to your outdoor space!